EF6使用.NET 4.5中引入的async和await关键字提供对异步查询和保存的支持。虽然不是所有的程序都能从异步获益,但当处理需要长时间运行、网络或受IO限制的任务时,异步可以用于提升客户端响应和服务器端的可伸缩性。
本篇包括如下主题:
何时真正使用异步
本演练的目的是介绍异步概念,使它易于观察异步和同步程序执行的区别,而不是为了说明异步编程提供好处的任何关键场景。
异步编程的重点在于当前托管线程等待一个操作时,要释放掉它来做其他工作。举个例子,当数据库引擎处理一个查询时,.NET代码什么都没有做。
在客户端程序(WinForms,WPF等)中,异步操作执行时,当前线程可以用来保持UI响应。在服务器端程序(ASP.NET等),线程可用来处理其他的入站请求。这可以减少内存使用或提高服务器的吞吐量。
使用异步的大多数程序不会有明显的好处,甚至还有害处。在提交之前,要使用测试、分析和常识衡量异步在特定场景下的影响。
这是学习异步的一些资源:
- Brandon Bray’s overview of async/await in .NET 4.5
- Asynchronous Programming pages in the MSDN Library
- How to Build ASP.NET Web Applications Using Async (includes a demo of increased server throughput)
创建模型
我们使用Code First创建模型和生成数据库,然而异步功能对包括EF设计生成的所有EF模型都有效。
- 创建一个控制台程序AsyncDemo
- 添加EntityFramework Nuget程序包
- 在解决方案资源管理器中,右击“AsyncDemo”项目
- 选择“管理NuGet程序包”
- 在管理NuGet程序包对话框中,选择“联机”,选择EntityFramework包
- 单击“安装”
- 添加一个Model.cs类,实现如下:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace AsyncDemo
{
public class BloggingContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
}
public class Blog
{
public int BlogId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual List<Post> Posts { get; set; }
}
public class Post
{
public int PostId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
public int BlogId { get; set; }
public virtual Blog Blog { get; set; }
}
}
创建同步程序
现在有了一个EF模型,下面来写一些代码使用它执行一些数据库访问。
- 修改Program.cs代码为如下内容
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace AsyncDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PerformDatabaseOperations();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Quote of the day");
Console.WriteLine(" Don't worry about the world coming to an end today... ");
Console.WriteLine(" It's already tomorrow in Australia.");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void PerformDatabaseOperations()
{
using (var db = new BloggingContext())
{
// Create a new blog and save it
db.Blogs.Add(new Blog
{
Name = "Test Blog #" + (db.Blogs.Count() + 1)
});
db.SaveChanges();
// Query for all blogs ordered by name
var blogs = (from b in db.Blogs
orderby b.Name
select b).ToList();
// Write all blogs out to Console
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("All blogs:");
foreach (var blog in blogs)
{
Console.WriteLine(" " + blog.Name);
}
}
}
}
}
这段代码调用PerformDatabaseOperations方法保存一个新的Blog到数据库并且从数据库中获取所有的Blogs,最后打印到控制台上。然后,程序写入a quote of the day到控制台。
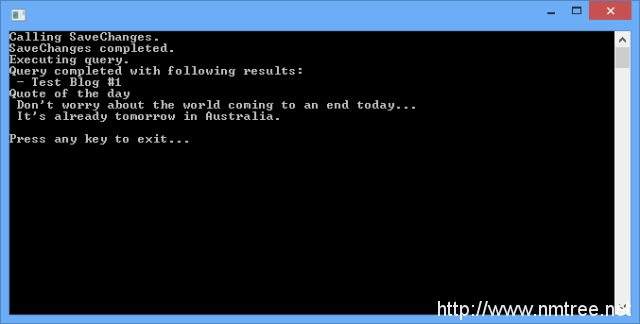
因为代码是同步的,执行程序可以看到下面的执行流程:
1.SaveChanges开始保存一个Blog到数据库
2.SaveChanges完成
3.查询所有的Blogs命令发送到数据库
4.查询返回,结果写到控制台
5.Quote of the day写到控制台
使其异步
现在程序运行正常,我们可以开始使用新的async和await关键字了。对Programs.cs作如下修改:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace AsyncDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var task = PerformDatabaseOperations();
Console.WriteLine("Quote of the day");
Console.WriteLine(" Don't worry about the world coming to an end today... ");
Console.WriteLine(" It's already tomorrow in Australia.");
task.Wait();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static async Task PerformDatabaseOperations()
{
using (var db = new BloggingContext())
{
// Create a new blog and save it
db.Blogs.Add(new Blog
{
Name = "Test Blog #" + (db.Blogs.Count() + 1)
});
Console.WriteLine("Calling SaveChanges.");
await db.SaveChangesAsync();
Console.WriteLine("SaveChanges completed.");
// Query for all blogs ordered by name
Console.WriteLine("Executing query.");
var blogs = await (from b in db.Blogs
orderby b.Name
select b).ToListAsync();
// Write all blogs out to Console
Console.WriteLine("Query completed with following results:");
foreach (var blog in blogs)
{
Console.WriteLine(" - " + blog.Name);
}
}
}
}
}
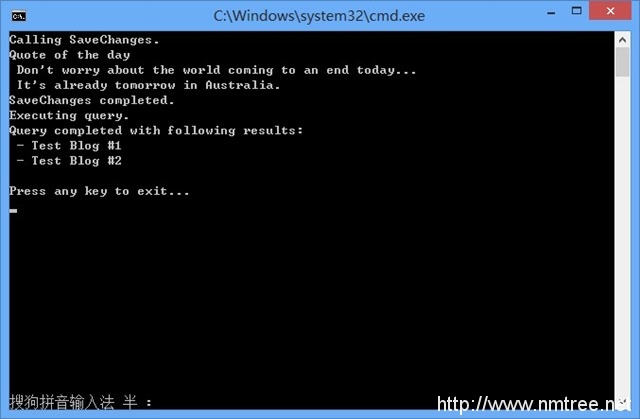
现在代码是异步的了,运行程序,可以观察一个不同的执行流程。
1.SaveChanges开始保存一个新的Blog到数据库
一旦命令发送到数据库,在当前托管线程上不再计算时间。PerformDatabaseOperations方法返回(即使还没有执行完),Main方法中的程序流程继续。
2.Quote of the day写入到控制台
因为在Main方法中没有其他工作要做,托管线程在Wait调用时阻塞,直到数据库操作完成。一旦完成,PerformDatabaseOperations剩余部分将被执行。
3.SaveChanges完成
4.查询所有Blogs命令发送到数据库
当查询在数据库里查询时,托管线程又一次空闲可以做其他工作。因为其他的执行都已经完成了,线程会在Wain方法调用时停止,直到查询完成。
5.查询返回,结果写入到控制台。
结束语
我们看到使用EF的异步方法是多么的简单。尽管通过简单的控制台程序异步的优势显现不出来,但是相同的策略可以应用到长时间运行或受网络限制的程序,或者引起大量线程增加内存占用的程序。



多表查询如何进行异步查询